- Anthony
When choosing the right microphone for your needs, you might not be sure which is better: analog vs digital wireless microphones. So what are the differences between analog and digital?
Analog wireless microphones operate on frequency coordination that can’t be detected by cell phones and other devices, while digital wireless mics broadcast their signal over a range of frequencies. These differences mean that digital wireless mics may have more interference than analog wireless systems do with nearby electronics.
We will explore these pros and cons in detail below so you can make an educated choice when purchasing your next mic! Please click here for our blog post Analog vs. Digital Wireless Microphone.
Analog vs Digital Wireless Microphone

Sound Quality
Digital wireless microphones sound less natural than analog wireless FM systems since digital compression and depending on the processing takes some high frequencies. Digital systems also can’t handle as much signal strength as analog wireless systems before distortion becomes evident.
Latency
Digital wireless microphone signals are processed by an encoding device that sends the digital signal over a digital RF channel, decoded by a decoding device connected to the respective microphone.
The digital wireless microphone system has an amount of latency (delay) because of depending on the processing of this multi-stage compared to an analog wireless microphone where only analog audio goes through modulation/demodulation, with no added circuitry in between.
A digital wireless system would be better for live theater or presentations where you need instant feedback from the audience, but not good for karaoke where lip sync is important.
The digital wireless microphone system is not recommended for singing or instruments since latency may cause you to miss notes or words in the performance due to latency from hitting the note or speaking your words. Digital systems also do not produce as much range compared to analog wireless mic FM systems.
RF Performance
Digital wireless microphones are great for permanent installs because they don’t have any interference problems like analog FM transmitters can have when too many units are used on the same frequency coordination at one time.
A digital wireless system can also be installed more easily than analog FM transmitters without going through a licensing agency and paying fees that could reach thousands of dollars per year depending on how many frequencies are needed.
Digital wireless microphone systems run their own companies like Shure and Sennheiser. They make these systems for their transmitters, while Alctron makes an RF Digital Wireless Radio System that works with any transmitter.
The digital wireless system also has a cleaner signal than analog wireless FM since it doesn’t have as much bandwidth used up by sidebands and noise like analog FM does.
Digital wireless microphone systems are best when you need to permanently cover a large area or install units where no frequencies could be shared because of other users in the same area.
It is not good if you’re using your unit at many different locations due to the higher cost of programming compared to an analog wireless microphone system.
Digital radio systems do not work well indoors because this wireless mic use line-of-sight transmission through UHF (ultra-high frequency) channels that don’t pass through objects and VHF (very high frequency) FM.
Digital wireless systems use more power than analog systems and have less range; overall, digital radio systems are best used for permanent installs.
You plan on using the same microphone or instruments at the same location daily without needing to move them often.
Security, or Encryption

The digital wireless system will have password protection for their channels so that no other company’s units can operate in your area.
Some digital wireless microphones come standard with 128-bit AES (advanced encryption standard) to keep your signal from being intercepted by any unauthorized people that may be listening on your channel.
Digital Wireless Radio Systems also work with RFID cards like HID iCLASS Cards – SecurID, which says what rights your cardholder has on the system. It can record who was using a specific microphone at any time and where it was located in case you need to do an investigation.
Digital wireless microphones are more secure than analog FM but won’t be as secure as IP audio systems.
Digital Wireless systems allow the user to set up passwords for access to channels and allows encryption of its data transmissions so that only those with authorized cards will have access.
Digital Wireless Microphone Systems are strongly recommended over Analog FM Microphone Systems because they provide better sound quality, security features and don’t share frequencies with other users.
Signal flow

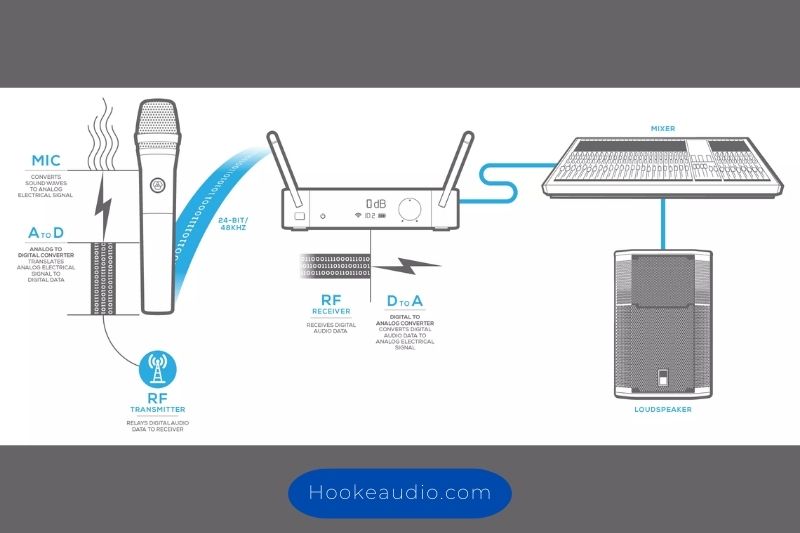
The fundamental difference between digital wireless microphones and analog wireless microphones lies in their signal flow. In analog wireless microphones, the audio signal is captured by the microphone’s transducer and then converted into an analog signal.
This analog signal is then modulated onto a carrier wave and transmitted wirelessly to a receiver. The receiver demodulates the signal and outputs the original analog audio signal.
In contrast, digital wireless microphones convert the audio signal into a digital format before transmission.
The analog audio signal is first converted into a digital signal using an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) inside the microphone. This digital signal is then modulated onto a carrier wave and transmitted wirelessly to a receiver.
The receiver demodulates the signal, converts it back to a digital signal, and then outputs the original audio signal.
The signal flow of digital wireless microphones includes additional steps compared to analog wireless microphones, such as the ADC and digital modulation.
However, this added complexity allows for benefits such as increased signal quality, better noise reduction, and improved signal-to-noise ratio.
Additionally, digital wireless microphones can transmit more data, which can be useful for transmitting additional information such as metadata or control signals.
Audio Bandwidth
Analog wireless microphones typically use FM modulation to transmit the audio signal. The analog signal is continuous and varies in frequency and amplitude, and the bandwidth of the signal is limited by the carrier frequency and the modulation scheme used.
Analog wireless microphones typically have a bandwidth of around 20 Hz to 20 kHz, which is the range of human hearing.
Digital wireless microphones, on the other hand, use digital signal processing to convert the analog audio signal into a digital signal before transmitting it.
The digital signal is then modulated and transmitted using various modulation schemes such as QPSK or QAM.
Digital wireless microphones typically have a much wider audio bandwidth than analog wireless microphones, with some models capable of transmitting up to 20 kHz to 20 kHz, which is the upper limit of human hearing.
Additionally, digital wireless microphones can also have a better signal-to-noise ratio and reduced interference from other wireless devices.
Signal-to-Noise Ratio

The Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) is a measure of the quality of a wireless microphone system. It represents the ratio of the desired signal to the background noise, and a higher SNR indicates a cleaner, clearer signal.
In general, digital wireless microphone systems have a higher SNR than analog systems. This is because digital systems convert the audio signal into a digital format, which allows for more sophisticated processing and error correction techniques that can help eliminate noise and interference.
Additionally, digital systems often use encryption and other techniques to ensure that the signal is transmitted securely and without interference.
Analog systems, on the other hand, rely on traditional analog modulation techniques, which are more susceptible to interference from other wireless devices and environmental factors. Analog systems can also suffer from signal degradation over long distances, resulting in lower SNR.
Media Versatility
Media versatility refers to the ability of a device to work with different types of media, such as different audio or video formats, and to transmit or receive them in different ways. In terms of digital wireless microphones versus analog ones, there are several differences in media versatility.
Digital wireless microphones typically have greater media versatility than analog microphones. This is because they can work with a wider range of digital audio formats and transmit data more efficiently.
They can also be used with other digital devices, such as mixers and recording equipment, without the need for conversion to analog signals.
Analog wireless microphones, on the other hand, have limited media versatility. They can only transmit analog signals and can only be used with analog devices, such as mixers and amplifiers.
This means that analog microphones may not be as compatible with newer digital equipment and may require additional conversion equipment to work with them.
Read more:
- Best Microphone For Youtube Videos
- Best Microphone For Live Vocals
- How Does A Dynamic Microphone Work And What Is It?
Video:
FAQs
Is digital wireless better?
Digital wireless systems generally have better audio quality in terms of frequency response and dynamic response. They also tend to be less noisy in end-of-range situations, as they can either be turned on or off, as with all things digital. The difference is more evident at lower- to mid-tier wireless.
What is the working principle of digital wireless microphones?
A wireless system works by converting an analog audio signal from the microphone into a radio wave frequency that can be transmitted to the receiver and then transforming it back into an audio signal that is output to the rest.
Is the toggle switch digital or analog?
A toggle switch cannot produce digital signals because it is analog. It can, however, be used as an input device with a device such as a microcontroller to produce digital signals that the microcontroller can interpret in 1’s or 0’s.
What does a wireless microphone mean?
It is also known as a radio microphone. The microphone body contains a small battery-powered radio transmitter that transmits audio from the microphone via radio waves to nearby receiver units, which then recover the audio. The receiver unit is connected by cable to any other audio equipment. It is called a wireless microphone system.
Conclusion
We hope you’ve enjoyed this comparison of analog and digital wireless systems. This is just a brief overview, but hopefully, it’s helped me understand the difference between these two different technologies: analog or digital.
Your selection moving forward will likely be less to do with better or worse and more to do with which one is right for your application.
You may find that there are other considerations as well, such as price point or power consumption – so make sure you take all factors into account before making your final decision!
For help deciding what communications technology best suits your needs, don’t hesitate to reach out to our team at Hooke Audio today!

